No language barriers!
A good opportunity to learn and practice TEI/XML together!
Contribute to an existing project and the fields of cinema studies, feminist DH, multilingual DH!
Intro:
Asian women’s images in the film industry have long been filtered through a Western male gaze and thus have been historically objectified as exotic and fetish beauties. Asian women filmmakers’ efforts also do not receive the same attention in a male-dominated film culture of auteurism. However, within the past few years, we have seen rising Asian women directors in the industry and their films gaining recognition. This project represents a step in the new direction of cinema feminist interventions. The primary objective of this project is to create a structured and organized database of Japanese women directors encoded by XML (Extensive Markup Language), making it easier to search and retrieve specific pieces of information on relevant subjects in their lives and works, such as education, employment, production, network, and social work. This project belongs to Phase 2 of the JWDP (The Japanese Women Directors Project), which seeks to enhance the accessibility and usability of our resources for scholars, educators, students, and the public. Unlike other TEI (Text Encoding Initiative) projects that annotate and store the structural elements in preexisting textual materials, our project is experimental to the extent that we are encoding research writings that we are currently making. The result of this project contributes to Phase 3 of the JWDP, which delivers our born-digital encoded content through a searchable database.
When we use the words “Japanese” and “women” to identify our research targets, we are referring to all directors self-identified as women, including Japanese women working outside Japan and non-Japanese women working in Japan. The JWDP has made significant progress in its Phase 1 on creating/publishing video interviews with scholars researching Japanese women filmmakers, collecting extensive materials on Japanese women directors’ profiles, and assembling a team of cinema specialists to execute the outreach plan to engage the public. The first trial of this project will be very specialized, covering a range of ten to fifteen Japanese women directors who make live-action narrative films. We hope to monitor the trial’s progress and expand the scope in a later stage to include women working on other genres, such as animation, documentaries, and experimental films.

Director list
- Please see the director list on the left. I hope to choose directors from the list with our potential team members. Although some materials are written in Japanese, most data have been collected and translated into English by previous efforts by the JWDP team and others. Also, for example, Naomi Kawase, Mika Ninagawa, and Miwa Nishikawa are very active in the international film market.
- I hope to include Japanese-American women directors as a focus for this course project. For example, we can explore works by Ruth Ozeki, Rea Tajiri, and Kayo Hatta together.
This project’s significant source of inspiration is DH initiatives that began in the SGML period. Find more information: Orlando: Women’s Writing in the British Isles from the Beginnings to the Present; Women Writer’s Online (WWO);WWP Lab;Women Film Pioneers Project
This project mainly stays at a textual level and limits its scope to organizing and producing textual entries and only uses XML elements/attributes, such as <mov> and <sound>, to encode video and audio materials’ metadata. Tools in MMIR (multimedia information retrieval) are beyond the scope of this project. But if any members are interested in MMIR, any new ideas are welcomed.
TEI: Founded in 1987, the Text Encoding Initiative (TEI) is a consortium that maintains and develops guidelines for encoding digital texts in the humanities. The current TEI guidelines provide a set of standardized XML rules and tags, known as TEI P5, for organizing and representing data in a structured framework. The TEI is also a community in which members in this community work on the improvement of the guidelines every year to address issues regarding non-hierarchical elements, overlapping hierarchies, normative bias, and ill-formed XML.
XML: XML uses tags to mark different elements in a document to produce both human-readable and machine-readable texts and is used widely in scholarly editing, manuscript transcribing, and computational text analysis. For example, for the women director profile pages, here is a minimal XML document encoding three directors’ names and birth years.
The start tag (e.g., <director>) marks the point in the sequence that an element starts, and the element closes with the end tag (e.g., </director>). We can also add attributes to the document. Here attribute values are specified for the <directorsList> element through the attributes xml: id and status. Later an XML processor can recognize this <directorList> as a draft instead of the final version, and the “list1” could label its element occurrence for later cross-reference works.
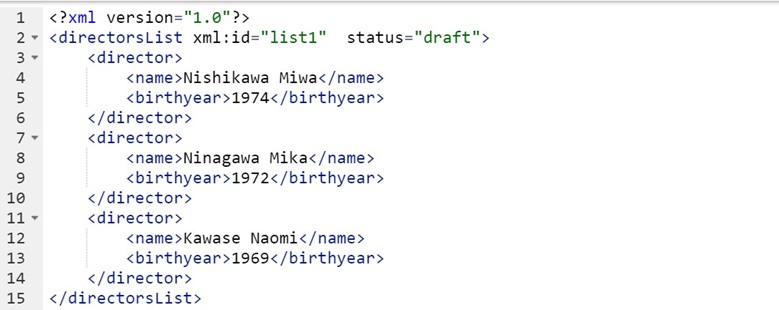
A minimal XML example
DTD: A Document Type Definition (DTD) is a set of rules that define the structure of an XML file. A well-formed XML document does not require a DTD and can just follow common rules but creating a DTD can ensure the integrity and consistency of the XML document. Our project will define elements, attributes, relationships, and constraints to customize the DTDs to give interpretive information in greater detail. Our project is a digital experiment searching for methods to create research-based DTD (Document Type Definition) that contain critical and interpretative tags generated by our research group, aligned with the structural tags officially recognized and produced by the TEI. Here is an example of the DTD we create to instruct the XML encoding in our project,
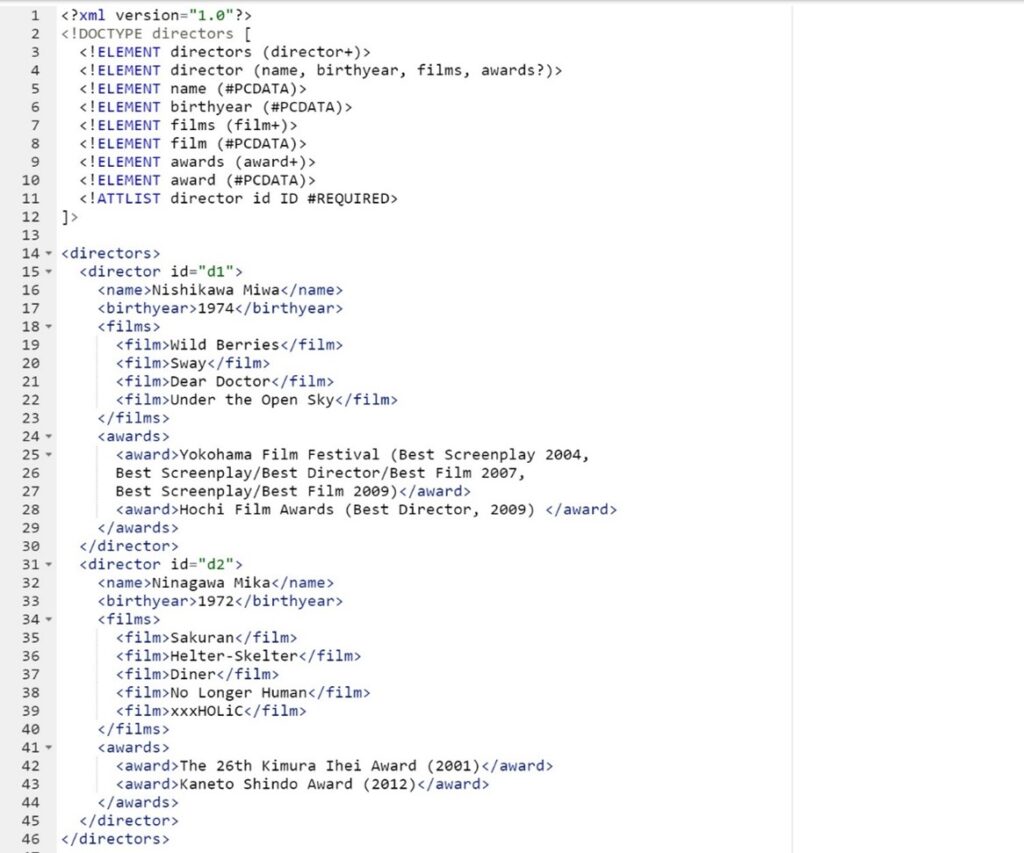
An example of the DTD
In this example, the DTD is defined within the DOCTYPE declaration. The DTD specifies that the document’s root element is <directors>. The root element can contain one or more <director> elements. Each <director> element must have an id attribute and can contain a <name>, a <birthyear>, a <films>, and an optional <awards> element. We then extract our markup directly from writing biographical sketches of Japanese women directors, transcribing/translating the interviews they receive, and editing scholarly writings on them. As a result, our tags not only deliver bio details on birth, name, family, education, and significant life events but also marks the contextual information on their career paths, such as team, co-worker, award, organization, company, funding, social movement, dual profession, etc. The final step (possibly will be started at end of phase 2 and remains a major task of phase 3) is to build a delivery system using XSLT, Java-related technologies, and Apache Tomcat that allows users to search and navigate the data we create.
Goals and outcomes:
The ultimate goal of this project is to build a searchable database and open the encoded data we create to the public. I also hope all potential members could learn and practice TEI/XML tools. The JWDP team is committed to releasing the encoded data of the first trial under the Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 License on its platform and through GitHub to allow the public to use, distribute, and build upon the project freely. We will also share our TEI/XML training materials by making a virtual workshop section on our website and encourage the modification of our tagsets and DTD by potential users.
For the work plan in the Spring semester, the main tasks will be research and writing on Japanese women directors, the DTD and tagsets building, and the XML encoding. All potential members will join the team to brainstorm appropriate tagsets to process the JWDP data and custom-design the XML tagsets and the DTDs. The project lead is responsible for writing the explanations of each tag with examples for the training session in TEI/XML.
- We aim to create a playground of DH aspects in Japanese women’s history and film studies for the public to support knowledge production and dissemination. The interface language and the primary language for displaying data are English.
- Instructors in the film studies programs could use the JWDP searching feature to prepare teaching materials on women filmmakers of color to update their syllabi. Students in film studies, area studies, and digital humanities could use the database to search for information on non-white/US-based women directors.
- Students will be able to extract the set of linked open data and apply computational methods to make network graphs, geospatial maps, and data visualizations. The database structure allows them to look into micro-level contextualized materials on these women’s lives and works and analyze macro-level trends outside established canons.
- Our goal to create feminist interventions in digital archives is inspired by Jacqueline Wernimont’s argument for an approach of feminist text encoding as political tools to present works done by marginalized groups; the idea of working on non-English speaking background materials is from Alan Liu’s suggestion on building multilingual digital humanities (DH) to “create a digitally tractable, extensible taxonomy of diversity” through building new database and renewing protocols.
Tentative team design:
Project and Research Lead: Miaoling Xue will serve as the project and research lead, monitoring the overall progress of the project, including team coordination, workflow/deadline management, and research progress.
Research and Metadata Coordinators: Classmate A/B/C will be the co-lead responsible for writing, categorizing and sorting data and working with the lead to do the team training in XML
Content Specialists: Graduate students in Japanese studies (UBC), researching women directors’ profiles, translating materials into English
Programmer: TBD, assisting in validating and delivering the XML file, testing the trial result using XSLT, Java-related technologies, and Apache Tomcat
Copy Editor: TBD
Consultants
Consultant on TEI (Text Encoding Initiative): Filipa Calado
Consultants on Japanese Cinema and Popular Culture: Colleen Laird (UBC), Catherine Munroe Hotes (KeioSFC/hosei_gis)
Further readings:
Liu, Alan. “Toward a Diversity Stack: Digital Humanities and Diversity as Technical Problem.” PMLA 135.1 (2020): 130–151.
The TEI Consortium. “TEI P5: Guidelines for Electronic Text Encoding and Interchange.” Last updated October 25, 2022. https://tei-c.org/release/doc/tei-p5-doc/en/Guidelines.pdf.
Wernimont, Jacqueline. “Whence Feminism? Assessing Feminist Interventions in Digital Literary Archives.” Digital Humanities Quarterly 7, no. 1 (2013). http://www.digitalhumanities.org/dhq/vol/7/1/000156/000156.html.


